This web page was produced as an assignment for Gen677 at UW-Madison Spring 2009
Gene Ontology
AMIGO was used to search for gene ontology relationships of NFATc1. The algorithm found 7 associations within humans. These included the following:
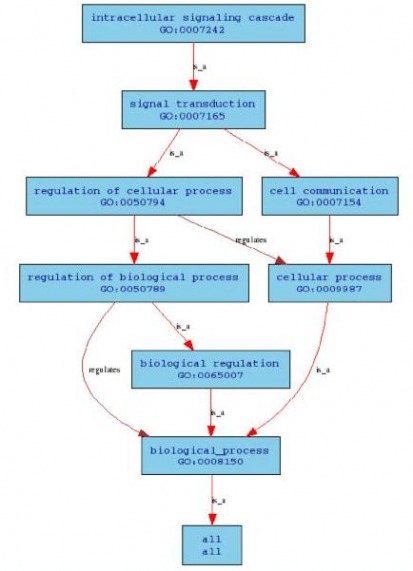
Biological Processes: Intracellular signaling cascade,
Regulation of transcription (DNA-dependent),
Transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
Cellular Component: Cytoplasm
Molecular Function: FK506 binding,
Transcription activator activity,
Transcription factor activity
All of the above terms make sense for NFATc1 and its function within a cell. NFATc1 belongs to a family of transcription factors so regulation of transcription and transcription factor/activator activity are appropriate. It also functions in an intracellular signaling cascade as show in Arron et al. through its interactions with calcineurin, DSCR1, and DYRK1A. It is a little surprising that the only cellular component reported was cytoplasm, as NFATc1 has been shown to occupy both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. As for the binding of FK506 (an immunosupressive drug) a query was done using DrugBank to further analyze this result. (See Chemical Genetics)
Three of these gene ontology terms were inferred from direct assay and the other four through traceable author statements. Below is an example of a tree-view for intracellular signaling cascade which has a relation to 4108 gene products. (Clicking on the figure below links out to the original tree-view of this biological process)
The same query in mice produced eleven associations, four of which were identical to those found in humans: intracellular signaling cascade, regulation of transcription (DNA-dependent), cytoplasm, and transcription activator activity.
Phenotypes
NFATc1 does not have a homolog in C. elegans or Drosophila so neither Wormbase nor FLYRNAi could be used for searching phenotypes of NFATc1. However, there is a homolg in zebra fish so ZFIN was utilized in an attempt to find related phenotypes. When a query of NFATc1 was used in the algorithm no phenotypes were reported.
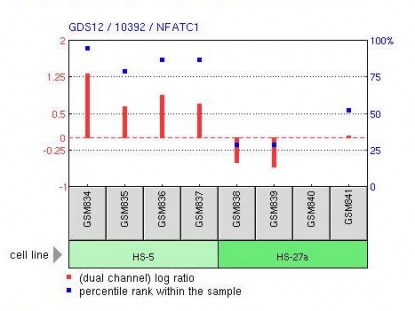
GEO was then used to investigate some gene expression profiles of NFATc1. An example is shown below.
This is a representation of an expression profile of NFATc1 in bone marrow stromal cell lines (HS-27a and HS-5) in humans. RNA samples from each line were analyzed to produce these results. As indicated by the red bars NFATc1 is up-regulated in HS-5 cells and down-regulated in HS-27a cells. This is just one example of many expression profiles for NFATc1.
Algorithmic Websites:
AMIGO: http://amigo.geneontology.org/cgi-bin/amigo/go.cgi
Wormbase: http://www.wormbase.org/
FLYRNAi: http://www.flyrnai.org/
ZFIN: http://zfin.org/cgi-bin/webdriver?MIval=aa-newmrkrselect.apg
GEO: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/
Margaret Noll, [email protected], last update 3/29/2009, http://www.gen677.weebly.com