This web page was produced as an assignment for Gen677 at UW-Madison Spring 2009
Amino Acid Sequence
The amino acid sequence of Isoform B of NFATc was obtained using NCBI and can be accessed through this link. (Links for the other four isoforms can be found on The Gene page of this website under the NFATc Isoforms.)
Protein Motifs
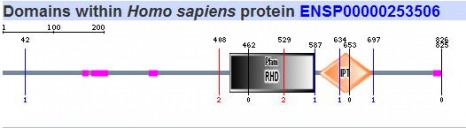
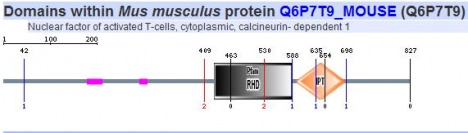
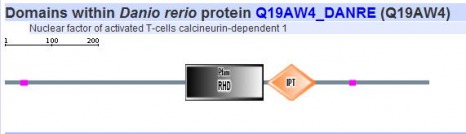
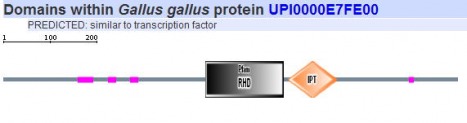
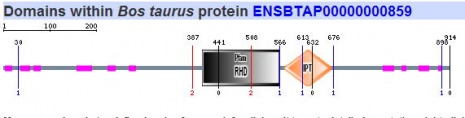
Since SMART gives results of both their database and PFAM it was the only program used here to search for respective protein motifs. The five homologs of NFATc were analyzed using this algorithm and the images can be seen below.
All five homologs showed the presence of the same protein motifs. Each one contained a RHD domain (Pfam algorithm) and an IPT domain (SMART algorithm). The RHD domain is found in a family of eukaryotic transcription factors, and phosporylation of this domain has been shown to regulate the expression of their target genes. (1) The IPT domain belongs to a family of proteins with an immunoglobulin like folds. These domains have been identified in intracellular transcription factors and it is directly involved in DNA binding. (2) The vertical blue lines seen in the diagrams of humans, mouse, and cow (above) indicate transmembrane domains, which supports the finding of integrin beta chains found in the DNA sequence. The red vertical line also shown on the aformentioned diagrams indicate signal peptides.
NFATc 3D Structure
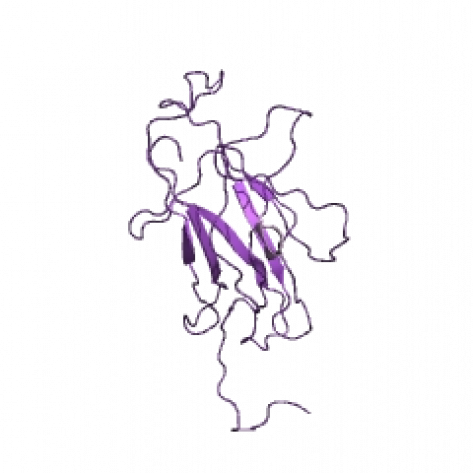
Above is the proposed 3D structure for NFATc in humans with 100% confidence (Information obtained using STRING). It has a very simple tertiary configuration containing only a few beta chains.
References:
1. EMBL-EBI (2006-2009) InterPro:IPR011539 Rel homolgy. Retrieved February 16, 2009 from http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/IEntry?ac=IPR011539
2. EMBL-EBI (2006-2009) Interpro: IPR002909 Cell surface receptor IPT/TIG Retrieved February 16, 2009 from http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/IEntry?ac=IPR002909
Algorithmic Websites:
NCBI: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=Protein&itool=toolbar
SMART: http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/
PFAM: http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/
STRING: http://string.embl.de/
*All the figures shown were generated using these algorithms
Margaret Noll, [email protected], last updated 4/26/2009, http://www.gen677.weebly.com